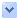Both fiber (which is filling) and exercise help combat obesity, which has been linked in several reports to the development of diverticulitis and diverticular bleeding.
Fiber content of various foods
|
|
Food
|
Serving size
|
Fiber (grams)
|
|
Fruits
|
|
Apple (with skin)
|
1 medium
|
4.4
|
|
Dates
|
1 cup
|
14.2
|
|
Pear (with skin)
|
1 medium
|
5.1
|
|
Prunes (dried, pitted)
|
1 cup
|
12.4
|
|
Raspberries
|
1 cup
|
11
|
|
Vegetables (cooked)
|
|
Artichoke
|
1 medium
|
10.3
|
|
Black beans
|
1 cup
|
15.0
|
|
Broccoli
|
1 cup
|
5.5
|
|
Brussels sprouts
|
1 cup
|
6.4
|
|
Carrots
|
1 cup
|
4.8
|
|
Chickpeas
|
1 cup
|
10.6
|
|
Lentils
|
1 cup
|
15.6
|
|
Lima beans
|
1 cup
|
13.2
|
|
Peas
|
1 cup
|
8.8
|
|
Pinto beans
|
1 cup
|
15.4
|
|
Squash (winter)
|
1 cup
|
5.7
|
|
Cereals and grains
|
|
All-Bran (Original)
|
cup
|
10
|
|
Amaranth (cooked)
|
1 cup
|
18.1
|
|
Barley (cooked)
|
1 cup
|
6
|
|
Bulgur wheat (cooked)
|
1 cup
|
8.2
|
|
Fiber One (Original)
|
cup
|
14
|
|
Oatmeal
|
1 cup
|
4
|
|
Quinoa (cooked)
|
1 cup
|
5.2
|
|
Shredded wheat
|
1 cup
|
6.4
|
|
Wild rice
|
1 cup
|
3.0
|
|
Nuts, seeds
|
|
Almonds (24 nuts)
|
1 oz
|
3.5
|
|
Peanuts (28 nuts)
|
1 oz
|
2.3
|
|
Pecans (20 halves)
|
1 oz
|
2.7
|
|
Sunflower seed kernels
|
cup
|
2.9
|
|
Source: USDA National Nutrient Database for Standard Reference, Release 23,
|
Diverticulitis and diverticular bleeding
Considering how many millions of Americans have diverticulosis, it's remarkable that complications are so rare. However, they do occur and can be serious. About 15% to 20% of people with diverticulosis develop diverticulitis — inflammation or infection of diverticula — and 5% to 15% experience diverticular bleeding.
Diverticulitis occurs when the wall of a diverticulum is eroded by pressure, trapped fecal matter, or both. If the damage is severe enough, a tiny perforation develops in the diverticulum and allows bacteria to infect the surrounding tissues. Usually, the body's immune system is able to confine the infection to a small area on the outside of the colon. But sometimes the infection develops into an abscess that erodes surrounding tissue, creating fistulas — passageways between the bowel and other structures in the abdominal cavity. Fecal material may spill out of the diverticulum into the abdominal cavity, causing peritonitis (infection of the peritoneum, the membrane that lines the abdominal cavity). Peritonitis is a critical condition that calls for prompt medical attention. Another situation requiring immediate investigation is diverticular bleeding, which occurs when pressure within an inflamed diverticulum erodes a blood vessel (see below).
Diagnosing diverticulitis. Diverticulitis can cause abdominal pain (usually worse in the lower left part of the abdomen), fever, and sometimes nausea. The inflamed area may be tender, and white blood cell count is usually elevated. The best test to confirm the diagnosis is a CT scan of the abdomen performed after you've received oral as well as intravenous contrast material. CT can show not only the extent and severity of the infection or inflammation but also complications such as peritonitis and fistula.
Treating diverticulitis. Antibiotics are the cornerstone of treatment. Because the colon harbors so many bacterial species, a broad range of bacteria must be targeted. A common approach is to prescribe metronidazole (Flagyl, generic) along with ciprofloxacin (Cipro, generic) or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim, generic). Another option is a combination of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid (Augmentin). Seven to 10 days of antibiotics will usually do the trick. People with mild-to-moderate diverticulitis can take their antibiotics in pill form at home; a liquid diet to rest the bowel is also important. Severe inflammation or complications usually require hospitalization and intravenous antibiotics. If you've been hospitalized, you'll be given fluids intravenously until you're well enough to switch to clear liquids and eventually a full diet.
Diverticulitis complications. If an abscess doesn't clear up when it is treated with antibiotics and bowel rest, it may need to be drained by means of a thin catheter inserted through the skin into the abscess and kept in place until the abscess has drained (this can take up to a month). Peritonitis (infection that has spread to the lining of the abdomen) may require both surgery and antibiotics. Fistula is less common than abscess formation and less urgent than peritonitis, but it, too, requires both surgery and antibiotics. As a last resort, when nothing else is effective, the inflamed segment of the colon may be removed.
Diverticular bleeding. The most common symptom is painless rectal bleeding that causes bright red or maroon bowel movements. This bleeding is usually mild and stops with bed rest. More massive bleeding is a medical emergency that calls for expert hospital care with blood transfusions and intravenous fluids. It also requires intensive efforts — using such techniques as colonoscopy or angiography — to locate the site of bleeding and stop it. If neither approach works, surgery may be needed.
文章定位: