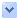對於以下新聞的一點點看法:
豈止是中國把美國當假想敵,中國早是美國想像中的大敵了。
美國保守派言論是如此,開放派言論也沒差多少。
以下文章只是中國假想敵言論中的代表罷了。
並不是我唯恐天下不亂,而是我一直有種感覺,
為了國際勢力消長,中國美國勢必一戰,問題只是戰場在哪而已?
統派總說台灣獨立,中國一定會打過來。
台灣不獨立,中國就不會打過來嗎?笑死人。要當鴕鳥也不是這樣當。
面臨的問題非常簡單:你是否要被中共這樣的政府統治?
我只能很明確的說:
2010年前,中國恐嚇武力犯台都是虛言,他們現在根本沒錢也沒能力打仗。
中國辦奧林匹克的錢已經被貪官污光了,胡錦濤因此焦頭爛額,這是台面上的消息。
以上言論是我的政治觀察與感言,不想跟任何人討論或辯論。
要在我留言版上跟我討論這事的朋友,我只能說抱歉了,我一定砍文。
---
The Illusion of 'Managing' China
By Robert Kagan
Sunday, May 15, 2005; Page B07
There has been much disc ussion recently about how to "manage the rise of China." The phrase itself is soothing, implying gradualism, predictability and time. Time enough to think and prepare, to take measurements of China's trajectory and adjust as necessary. If China eventually emerges as a clear threat, there will be time to react. But meanwhile there is time enough not to overreact, to be watchful but patient and not to create self-fulfilling prophecies. If we prematurely treat China as an enemy, it is said, it will become an enemy.
The idea that we can manage China's rise is comforting because it gives us a sense of control and mastery, and of paternalistic superiority. With proper piloting and steady nerves on our part, the massive Chinese ship can be brought safely into harbor and put at anchor. It can be "integrated" into the international system and thereby tamed and made safe for civilized existence in the postmodern world. Wisely "managed," China can be a friend. Badly managed, it can become a very dangerous power indeed. But at least the choice seems to be ours.
Chinese students at the Tongji University in Shanghai receive compulsory military training, August 29, 2004. Chinese university students are all required to go through military training to improve patriotism and self discipline. REUTERS/China Photos (Students At Tongji University In Shanghai Receive Compulsory Military Training./reuters)
The history of rising powers, however, and their attempted "management" by established powers provides little reason for confidence or comfort. Rarely have rising powers risen without sparking a major war that reshaped the international system to reflect new realities of power. The most successful "management" of a rising power in the modern era was Britain's appeasement of the United States in the late 19th century, when the British effectively ceded the entire Western Hemisphere (except Canada) to the expansive Americans. The fact that both powers shared a common liberal, democratic ideology, and thus roughly consonant ideas of international order, greatly lessened the risk of accommodation from the British point of view.
Other examples are less encouraging. Germany's rise after 1870, and Europe's reaction to it, eventually produced World War I. Even the masterly Bismarck, after a decade of successful German self-management, had a difficult time steering Europe away from collision. The British tried containment, appeasement and even offers of alliance, but never fully comprehended Kaiser Wilhelm's need to challenge the British supremacy he both admired and envied. Right up until the eve of war, highly regarded observers of the European scene believed commercial ties among the leading powers made war between them unlikely, if not impossible.
Japan's rise after 1868 produced two rounds of warfare -- first with China and Russia at the turn of the century, and later with the United States and Britain in World War II. The initial Anglo-American response to Japan's growing power was actually quite accommodating. Meiji Japan had chosen the path of modernization and even Westernization, or so it seemed, and Americans welcomed its ascendancy over backward China and despotic Russia. Then, too, there was the paternalistic hope of assisting Japan's entry into the international system, which was to say the Western system. "The Japs have played our game," Theodore Roosevelt believed, and only occasionally did he wonder whether "the Japanese down at bottom did not lump Russians, English, Americans, Germans, all of us, simply as white devils inferior to themselves . . . and to be treated politely only so long as would enable the Japanese to take advantage of our national jealousies, and beat us in turn."
Today we look back at those failures and ruminate on the mistakes made with the usual condescension that the present has for the past. But there is no reason to believe we are any smarter today than the policymakers who "mismanaged" the rise of Germany and Japan. The majority of today's policymakers and thinkers hold much the same general view of global affairs as their forebears: namely, that commercial ties between China and the other powers, especially with Japan and the United States, and also with Taiwan, will act as a buffer against aggressive impulses and ultimately ease China's "integration" into the international system without war. Once again we see an Asian power modernizing and believe this should be a force for peace. And we add to this the conviction, also common throughout history, that if we do nothing to provoke China, then it will be peaceful, without realizing that it may be the existing international system that the Chinese find provocative.
The security structures of East Asia, the Western liberal values that so dominate our thinking, the "liberal world order" we favor -- this is the "international system" into which we would "integrate" China. But isn't it possible that China does not want to be integrated into a political and security system that it had no part in shaping and that conforms neither to its ambitions nor to its own autocratic and hierarchical principles of rule? Might not China, like all rising powers of the past, including the United States, want to reshape the international system to suit its own purposes, commensurate with its new power, and to make the world safe for its autocracy? Yes, the Chinese want the prosperity that comes from integration in the global economy, but might they believe, as the Japanese did a century ago, that the purpose of getting rich is not to join the international system but to change it?
We may not know the answers to these questions. But we need to understand that the nature of China's rise will be determined largely by the Chinese and not by us. The Chinese leadership may already believe the United States is its enemy, for instance, and there is nothing we can do to change that. Partly this is due to our actions -- such as the strengthening of the U.S.-Japanese military alliance, which began during the Clinton administration, and our recent efforts to enhance strategic ties with India. Partly it is due to our different forms of government, since autocratic rulers naturally feel threatened by a democratic superpower and its democratic allies around their periphery. Partly it is due to the nature of the situation in East Asia. It used to be an article of faith among Sinologists that the Chinese did not want to drive the United States out of the region. Today many are not so sure. It would not be unusual if an increasingly powerful China wanted to become the dominant power in its own region, and dominant not just economically but in all other respects, as well.
When one contemplates how to "manage" that, however, comforting notions of gradualness, predictability and time begin to fade. The obvious choices would seem to lie between ceding American predominance in the region and taking steps to contain China's understandable ambitions. Not many Americans favor the former course, and for sound political, moral and strategic reasons. But let's not kid ourselves. It will be hard to pursue the latter course without treating China as at least a prospective enemy, and not just 20 years from now, but now. Nor, if that is the choice, can Chinese leaders be expected to wait patiently while the web of containment is strengthened around them. More likely, they will periodically want to challenge both the United States and its allies in the region to back off. Crises could come sooner than expected, and without much warning, requiring difficult judgments about the risks and rewards of both action and inaction.
That is likely what the future holds. The United States may not be able to avoid a policy of containing China; we are, in fact, already doing so. This is a sufficiently unsettling prospect, however, that we are doing all we can to avoid thinking about it. We conjure hopeful images of a modernizing China that seeks only economic growth and would do nothing to threaten commercial ties with us -- unless provoked -- even as we watch nervously the small but steady Chinese military buildup, the periodic eruptions of popular nationalism, the signs of Chinese confidence intermingled with feelings of historical injustice and the desire to right old wrongs.
Which China is it? A 21st-century power that wants to be integrated into a liberal international order, which would mean both a transformation of its own polity and a limitation of its strategic ambitions? Or a 19th-century power that wants to preserve its rule at home and expand its reach abroad? It is a worthy subject for debate, because the answer will determine the future as much as or more than anything we do. But it is unlikely we will have a definitive answer in time to adjust, to "manage" China's "rise," any more than our predecessors did. As in the past, we will have to peer into the fog and make prudent judgments, informed by the many tragic lessons of history.
Robert Kagan, a senior associate at the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace, writes a monthly column for The Post.
文章定位: